By Kelly House, Bridge Michigan
The Great Lakes News Collaborative includes Bridge Michigan; Circle of Blue; Great Lakes Now at Detroit PBS; Michigan Public, Michigan’s NPR News Leader; and who work together to bring audiences news and information about the impact of climate change, pollution, and aging infrastructure on the Great Lakes and drinking water. This independent journalism is supported by the Charles Stewart Mott Foundation. Find all the work HERE.
- Plastic pollution is a large and growing problem in the Great Lakes, according to a new report
- Data from beach cleanups shows 86% of trash collected is plastic
- Report authors are calling for more regulations on single-use plastic production and use
In news unlikely to surprise Great Lakes beachgoers, plastic litter is a large and growing problem in the lakes.
A new report from the Alliance for the Great Lakes adds a new data point to the growing body of evidence that America’s plastic addiction and waste-disposal habits are polluting our land and water.
The Chicago-based group analyzed 20 years of data from 14,000 volunteer beach cleanups across the region, finding that 86% of litter collected is composed at least partially of plastic.
Since the group’s Adopt-a-Beach program’s inception 1991, more than 200,000 volunteers have removed 9.7 million pieces of litter, amounting to more than 535,000 pounds, from Great Lakes beaches.
Olivia Reda, the report’s author and a volunteer engagement manager for the alliance, said the data emphasizes the need to better regulate plastic pollution in the Great Lakes and beyond.
“We need to address this issue in a systemic way,” Reda said. “We need to reduce production of single-use plastics and hold producers responsible for the waste that their products generate.”
Why it matters
The Great Lakes are the region’s most prized natural resource, and are expected to become all the more valuable as climate change increases water scarcity in many other parts of the world. They provide habitat for a wide array of species and drinking water for 40 million people in the U.S. and Canada.
And as Bridge has reported, plastic litter tends to break down into tiny pieces known as microplastics, which are both dangerous and difficult to clean up. Those tiny particles are now so ubiquitous in the environment that they have turned up in human breast milk and blood. Exposure is associated with cancer, fertility issues and developmental issues.
Despite the risks, chemical companies are producing — and consumers are using — more plastic every year.
That, along with greater attention to tiny plastic pieces during beach cleanups, has correlated with a shift in the makeup of Great Lakes beach trash over time. Before the past decade, cigarette butts were the most common item. Now, small plastic pieces under 2.5 centimeters come in first — representing 40 percent of all litter— followed by cigarette butts, foam, bottle caps and food wrappers.
Once you begin to notice the microplastics problem, Reda said, “you can’t unsee it.”
“You start to notice it all over the environment.”
Other studies have produced similar results. According to the United States Geological Survey, there are 112,000 particles of microplastics per square mile of Great Lakes water.
In total, 22 million pounds of plastic waste enters the Great Lakes annually, according to a study by researchers at the University of Wisconsin-Madison.
Food containers and nurdles
Much of the problem comes from single-use plastics, or products designed to be used only once and then thrown away. In the Alliance for the Great Lakes study, 27 percent of waste came from food-related items such as takeout containers, straws, bottle caps and wrappers.
The report’s authors urged action from businesses and governments. Their proposed solutions include “extended producer responsibility” policies, which hold plastics manufacturers responsible for the pollution caused by their products.
Cutting back on single-use plastics would also help curb the flow of waste, and Michigan Democratic lawmakers have vowed to lift a Republican-imposed “ban on bans” that prevents local governments from regulating plastic grocery bags. If the ban is lifted, communities like Ann Arbor and Detroit have expressed an interest in passing policies to discourage plastic bag use.
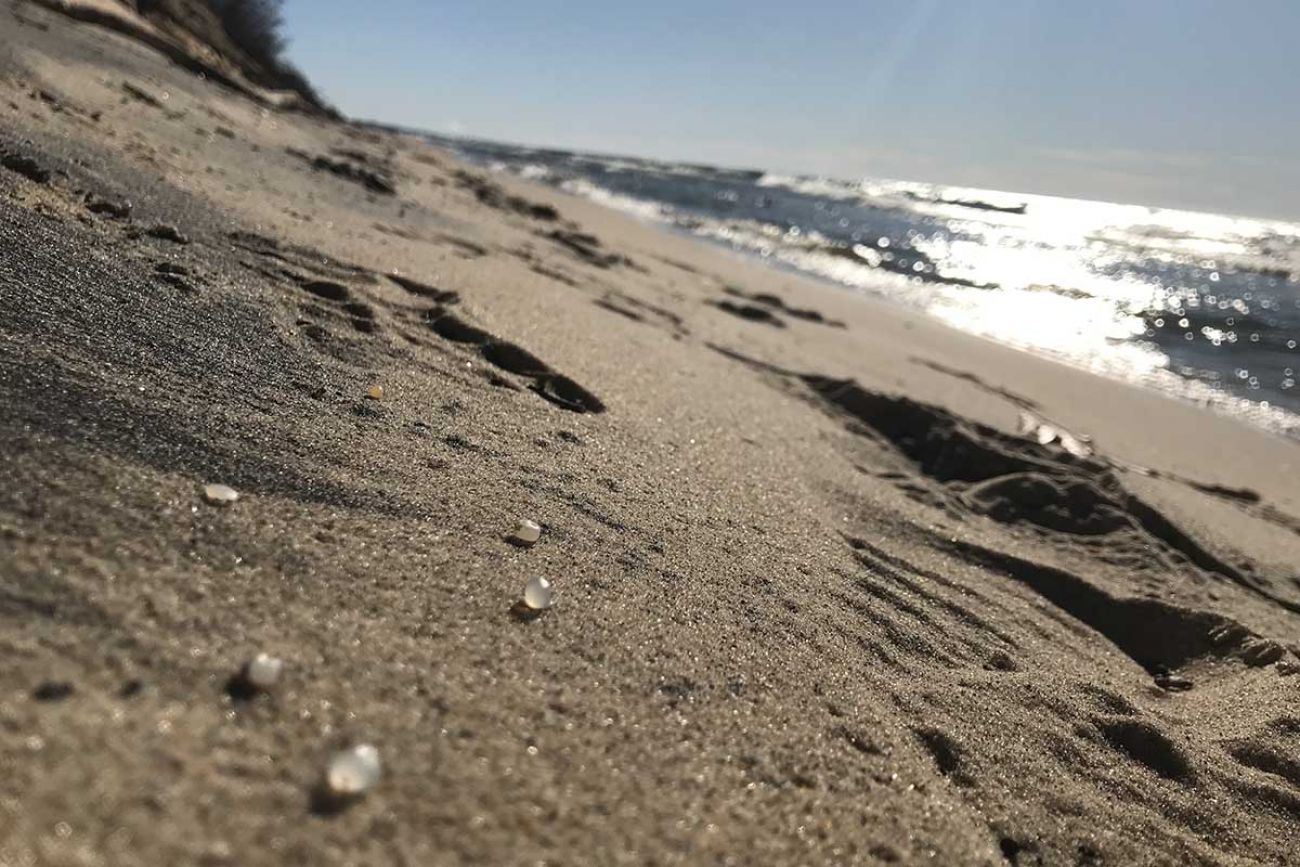
Industrial policy plays a role, too. Much of the plastic waste on Great Lakes beaches comes from nurdles, or small plastic pellets that are melted down to create products like water bottles. Those pellets sometimes fall off Great Lakes freighters and into the water, and advocates argue companies should face penalties for such pollution.
Opponents of those efforts argue they will raise prices for businesses and their customers.
Catch more news at Great Lakes Now:
Michigan gets $290M boost for water upgrades as Flint crisis anniversary nears
Good news for Michigan smelt season: PFAS levels lower than feared
Featured image: “Nurdles” scattered on the Lake Michigan shoreline near Muskegon. Nurdles are the small plastic pellets that are melted down to produce plastic products, and are a common type of microplastic. (Bridge photo by Kelly House)