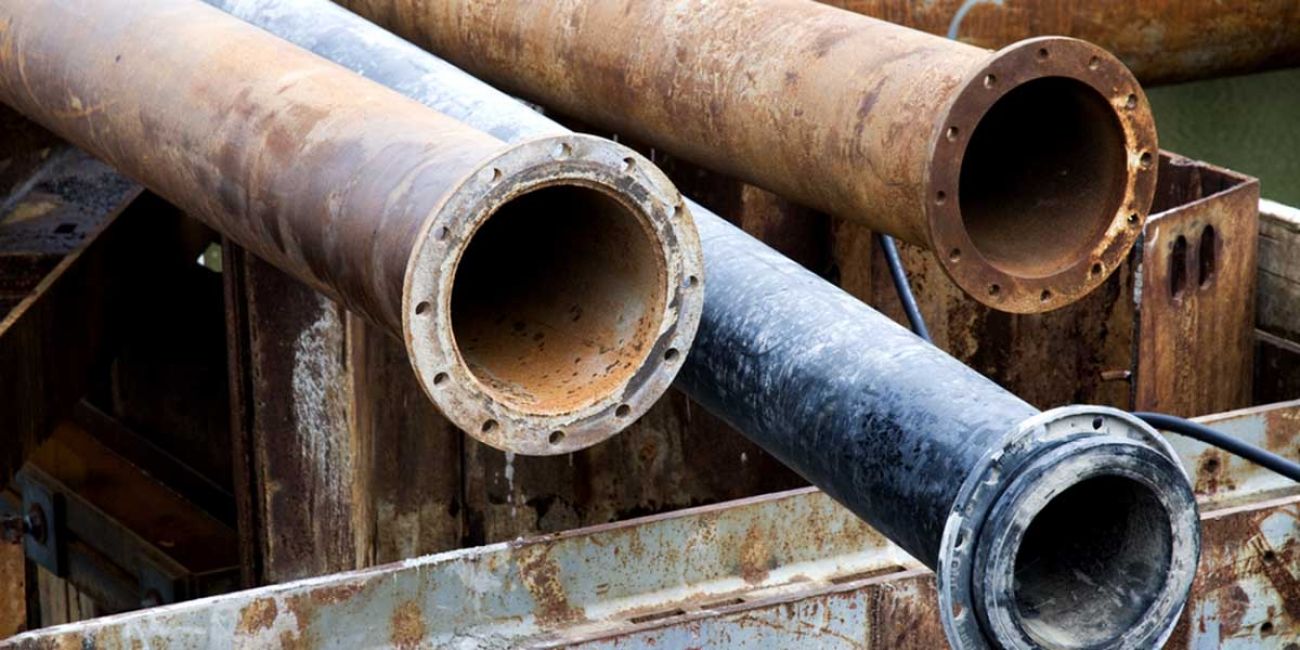
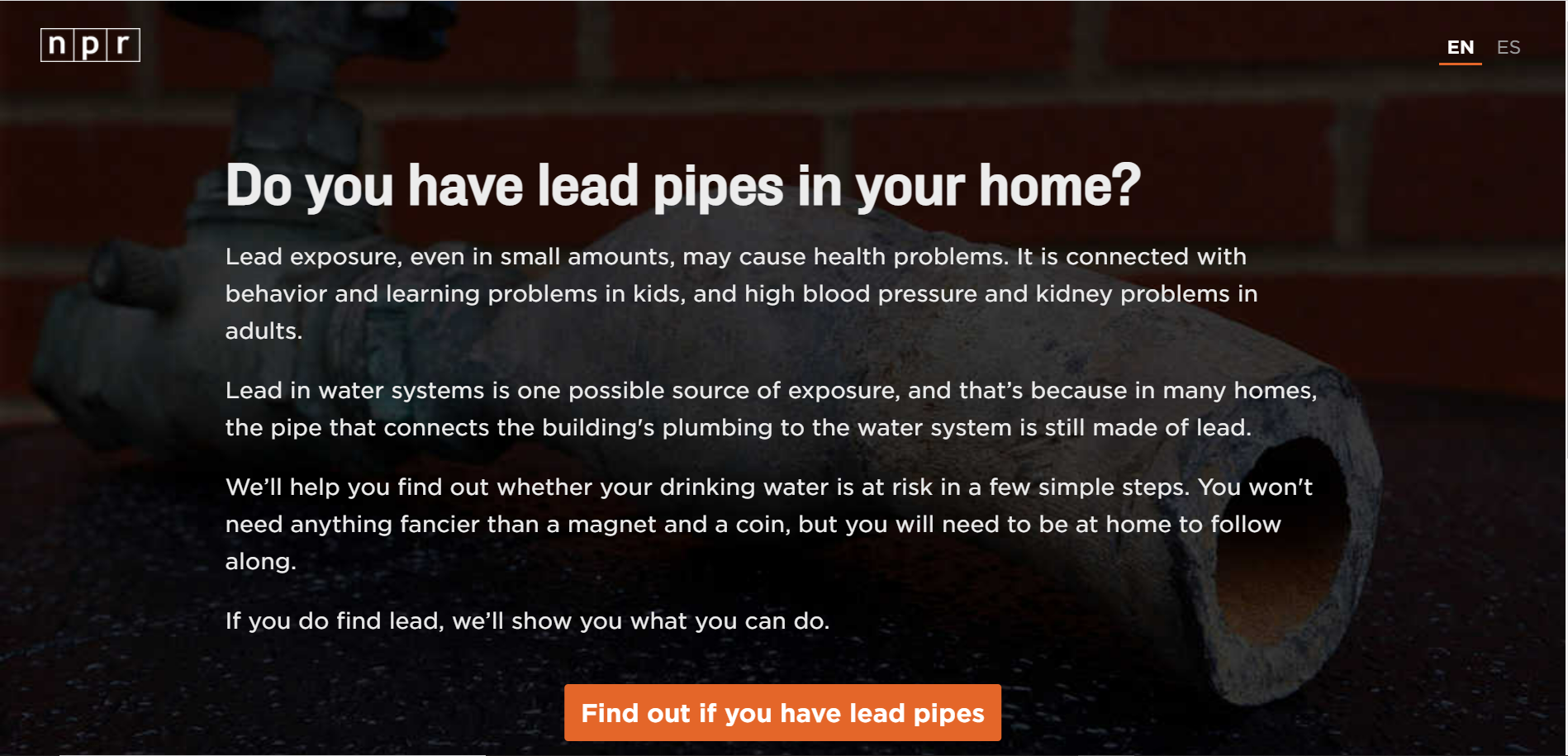
The harmful effects of lead are well known. When consumed, it can damage childrens’ brains and nervous systems, stunt their growth and affect their ability to focus. Children with high levels of lead in their blood are more likely to drop out of school or have brushes with the law. For adults, it’s linked to high blood pressure and kidney problems.
NPR developed a tool to make it easier for you to check if your drinking water is at risk for lead exposure and what kinds of solutions are available to you if that’s the case. Follow the steps to learn more about the pipes in your home.
For all of Great Lakes Now’s coverage of lead in drinking water – including the current crisis in Benton Harbor, Michigan – click HERE.
Click on the photo to use the NPR tool:
Catch more news on Great Lakes Now:
Why are so many Michigan water systems finding lead? They’re looking harder
Seven Years On: The Flint water crisis has yet to conclude
Featured image: Lead service lines in old cities’ drinking water systems are far from the only culprit contributing to childhood lead exposure in Michigan. Paint flakes and dust are the leading sources of lead poisoning. (Bridge file photo)